ISC Question Paper 2009
Computer Science
Class XII
General Instruction:
(i). All working including rough work should be done on the same sheet as, and adjacent to the rest of the answer.
(ii). The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets []. (Material to be supplied: Log tables including Trigonometric functions)
(iii). A list of useful physical constants is given at the end of this paper.
PART I
Attempt all questions from this Section
1. (a) Obtain the Truth Table to verify the following expression: x.(y+z) = x.y + x.z Also name the law stated above. [2]
(b) Answer the following questions related to the gate given below:
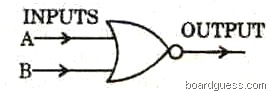
(i) What is the output of the above gate if input A = 0, B = 1?
(ii) What are the values of the inputs if output = 1? [2]
(c) Given F = A + (B+C). (D'+E)
Find F' and show the relevant working in steps. [2]
(d) State the dual for the following expression and also draw the logic gate diagram for the dual expression obtained using NOR gate only.
P = A.B + C.D [2]
(e) For the given truth table where A, B, C are inputs and X is the output,
| A | B | C | X |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Write:
(i) Canonical sum-of-product expression (SOP)
(ii) Canonical Product-of-Sum expression (POS)
2. (a) State a difference between Linear and Non-Linear Data Structure. Give one example of each. [2]
(b) Convert the following infix expression to its postfix form : [2]
( (P*Q) / (R / S+T)) + U
(c) Simplify the following expression by using the Boolean laws. Show the working in steps and also mention the laws used: [2]
x'.y'.z' + x'.y'.z + x'y.z + x'.y.z' + x.y'.z + x.y'z
(d) Each element of an array A[20][10] requires two bytes of storage. If the address of A[6][8] is 4000, find the Base Address at A[0][0] when the array is stored as Row Major wise. [2]
(e) Define Inheritance. How is it useful in programming?
Q3. (a) The following function trial() and perform() are a part of some class. Answer the following parts given below. Show the dry run/working. int trial (int n)
{
return 2;
else if (n==2)
return 3;
else
return trial (n-2) + trial (n-1);
}
| //for C++// void perform (int p) { int x; for(int i=1 ; i<=p; i++) OR x=trail (i); cout<<x<<" "; } } | OR | //for Java// void perform (int p) { int x; for (int i=1 ; i<p; i++) { x=trail (i); System.out.print(x + “”); } } |
(i) What will the function trial () return when the value of n is 4? [2]
(ii) What will be the output of the function perform () when the value of p is 5? [1]
(iii) In one line state what the function trial () is doing, apart from recursion? [1]
(b) Answer the following from the diagram of a Binary Tree given below:
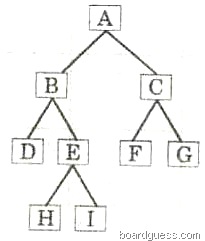
i) Root of the tree [1]
ii) External nodes of the tree. [1]
iii) List the nodes in the tree using Inorder Traversal. [1]
iv) Left subtree. [1]
v) Height of the tree. [1]
Section A
4. (a) F(P,Q,R,S) = P’Q’RS' + P'QRS' + PQ’R'S + PQ’RS' + PQ’RS + PQR'S + PQRS' + PQRS [5]
Use Karnaugh's Map to reduce the given function F using the SOP form. Draw a logic gate diagram for the reduced SOP form. You may use gate with more than two inputs. Assume that the variables and their complements are available as inputs.
(b) F(A,B,C,D) = n(0,1,2,3,5,7,9,13) [5]
Use Karnaugh's Map to reduce the given function F using the POS form. Draw a logic gate diagram for the reduced POS form. You may use gate with more than two inputs. Assume that the variables and their complements are available as inputs.
5. A provisional store announces a special discount on all its product as a festival offer only to those who satisfy any one of the following conditions :
• If he/she is an employee of the store and has a service of more than 10 years.
OR
• If he/she is a regular customer of the store whose age is less than 65 years and is not an employee of the store.
OR
• If he/she is a senior citizen but not a regular customer of the store.
The inputs are :
E : Employee of the store
R : Regular customer of the store
S : Service of the employee is more than 10 years
C : Senior citizen of 65 years or above
Output •
X-Denotes eligible for discount [1 indicates YES and 0 indicates NO in all cases]
(a) Draw the truth table for the inputs and outputs given above and write the SOP expression for X(E,R,S,C). [5]
(b) Reduce X(E,R,S,C) using Karnaugh’s Map [5]
Draw te logic gate diagram for the reduced SOP expression for X(E,R,S,C) using AND & OR gates. You may use gates with two or more inputs. Assume that the variable and their complements are available as inputs.
------------------- Please go to next page ---------