INSURANCE
CLASS-XI
SEMESTER-I
PART-I
I. Concept of Risk:- Types of risks, methods of handling risk, functions of insurance, scope of insurance. History of Insurance, Indian market structure, legislative measures, insurance legislation and other legislation relating to insurance agency, licensing, commission structure, loss prevention; stamp duty.
PART-II
III. (a) Underwriting:- New business procedure, proposal from cover note, certificate of Insurance, co-insurance; renewal procedure, premium.
SEMESTER-II
PART-I
I. Law of Contract:- Essentials of Insurance contracts, validity of contract, Basic principles of insurance, utmost good faith, insurable interest, indemnity, subrogation, contribution, proximate cause.
PART-II
III. (b) Claims:- Factors to be considered, arbitration procedure, methods of settlement. Re-insurance; method, application.
IV. Accounting Practices:- Forms of Accounts, reserves for unexpired risks practice, statutory returns.
IV. Salesmanship; Qualities of Salesman, technique of selling, method of canvassing.
MATHEMATICS
CLASS- XI
SEMESTER- I
Unit-1: SETS AND FUNCTIONS
1. Sets:
Sets and their representations. Empty & Infinite sets. Equal sets, subjects, Subsets of the set of real numbers especially intervals (with notations). Power set, Universal set, Venn diagrams, Union and Intersection of sets, Difference of sets,
Complement of a set.
2. Relations & Functions:
Ordered pairs, Cartesians product of sets. Number of elements in the Cartesian product of two finite sets. Cartesian product of the reals with itself (upto R x R x R). Definition of relation, pictorial diagrams, domain, co-domain and range of a relation. Function as a special kind of relation from one set to another. Pictorial representation a function, domain, co-domain range of a function. Real valued function of the real variable, domain and range of these functions, constant,
identity, polynomial, rational, modulus, signum and greatest integer functions with their graphs. Sum, difference, product and quotients of functions.
Unit-II: ALGEBRA
1. Principle of Mathematical Induction:
Processes of the proof by induction, motivating the application of the method by looking at natural numbers as the least inductive subset of real numbers. The principle of mathematical induction and simple applications.
2. Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations:
Need for complex numbers, especially −1 to be motivated by inability to solve every quadratic equation. Brief description of algebraic properties of complex numbers. Argand plane and polar representation of complex numbers. Statement of Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, solution of quadratic equations in the complex number system.
3. Linear Inequalities:
Linear inequalities, Algebraic solutions of linear inequalities in one variable and their representation on the number line. Graphical solution of linear inequalities in two variables. Solution of system of linear inequalities in two variables graphically.
4. Sequence of Series:
Sequence and Series, Arithmetic progression (A.P.), arithmetic mean (A.M.), Geometric progression (G.P.), general term of a G.P., sum of n terms of a G.P. Geometric mean (G.M.), relation between A.M. and G.M. Sum to n terms of the
special series n, n2 and n3 .
Unit IV: CALCULUS
1. Limits and Derivatives:
Derivatives introduced as rate of change both as that of distance function and geometrically, intuitive idea of limit. Definition of derivative, relate it to slope of tangent of the curve, derivative of sum, difference, product and quotient of functions. Derivatives of polynomial and trigonometric functions
SEMESTER II
Unit-1: SETS AND FUNCTIONS
1. Trigonometric Functions
Positive and negative angles. Measuring angles in radians & in degrees and conversion from one measure to another. Definition or trigonometric functions with the help of unit circle. Truth of the identity sin2x+cos2x =1, for all x. Signs of trigonometric functions and sketch of their graphs. Expressing sin (x+y) and cos (x+y) in terms of sinx, siny, cosx &
cosy, Deducing the identities like following.
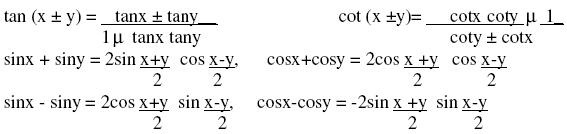
Identities related to sin2x, cos2x, tan2x, sin3x, cos3x and tan3x. General solution of
trigonometric equations of the type ![]() Proofs and simple applications of sine and cosine formulae.
Proofs and simple applications of sine and cosine formulae.
Unit-II ALGEBRA
1. Permutations & Combinations:
Fundamental principle of counting, Factorial n. Permutations and combinations, derivation of formulae and their connections, simple applications.
2. Binomial Theorem:
History, statement and proof of the binomial theorem for positive integral indices. Pascal's triangle, general and middle term in binomial expansion, simple applications.
Unit-III: COORDINATE GEOMETRY
1. Straight Lines:
Brief recall of 2D from earlier classes, slope of a line and angle between two lines. Various forms of equations of a line: parallel to axes, point-slope form, slop-intercept form, two-point form, ntercepts form and normal form. General equation of a line, Distance of a point from a line.
2. Conic Sections:
Sections of a cone; circles, ellipse, parabola, hyperbola, a point, a straight line and pair of intersecting lines as a degenerated case of a conic section. Standard quations and simple properties of parabola, ellipse and hyperbola. Standard
equation of a circle.
3. Introduction to Three-dimensional Geometry
Coordinate axes and coordinate planes in three dimensions. Coordinates of a oint. Distance between two points and section formula.
Unit-V: MATHEMATICAL REASONING
1. Mathematical Reasoning:
Mathematically acceptable statements. Connecting words/phrases-consolidating he understanding of "if and only if (necessary and sufficient) condition", implies", "and/or", "implied by", "and", "or", "there exists" and their use through
variety of examples related to real life and Mathematics, Validating the statements nvolving the connecting words-difference between contradiction, converse and ontapositive.
UNIT-VI: STATISTICS & PROBABILITY
1. Statistics:
Measure of dispersion: mean deviation, variance and standard deviation of ngrouped/grouped data. Analysis of frequency distributions with equal means ut different variances.
Probability:
Random experiments: outcomes, sample spaces (set representation). Events: ccurrence of events, 'not', 'and' and 'or' events, exhaustive events, mutually xclusive events. Axiomatic (set theoretic) probability, connections with the
theories of earlier classes. Probability of an event, probability of 'not', 'and' & 'or' vents.
MODERN OFFICE PRACTICES
CLASS-XI
SEMESTER-I
Rationale
The main objectives of the course in modern office practice is to make the tudents understand the concepts and principles of office methods and procedures and evelop skills in performing office operations. This subject aims at making the students ell conversant with the services provided by a modern office and enables them to resent the same using modern methods and equipments.
PART-A
Introduction of Office
Meaning and Evolution of Modern Office, Functions of Office, Place of Office in a Modern Business Organisation, Concept of Office Management, Departments of a Large Office, Role and Qualities of a Modern Office Manager.
PART-B
Office Communications
Meaning and importance of Effective Communication, Principles of Communication, Channels of Communication, Role of Manager in Effective Communication, Types of Phone Calls, Video Conferencing, Effective Letter Writing, E-mail Writing and Report Writing.
PRACTICAL
Communication skills (Resume Writing and Application for jobs).
SEMESTER-II
PART-A
Office Machines
Meaning and Relevance of Office Automation, Types of Machines used in Office
with Special Emphasis on use of Computers in Office, Hardware and Software (MSOffice-
MS Word, MS Excel, MS Power Point and MS Outlook), Types and use of
Printers, Scanners, Copiers and other Appliances.
PART-B
Office Record Management
Meaning and Features of Record Management, Filing: Characteristics of a good filing system; Classification of Records for Filing (Alphabetical, Numerical etc.), Modern Methods-Vertical, Horizontal, lateral and suspensions; Equipment; Types of Files; Filing routine, Disposal of Obsolete Documents; Indexing: Importance; Types-Page Index; Card Index; Strip Index; Rotary Index, Micro Filing: Merits and Demerits; Types-Roll Film, Fiche, Jackets etc. Meaning of Electronic Filing, Data Storage Management.
PRACTICAL
Students will be imparted a practical knowledge regarding basics of computers.
Operation of Scanners, Printers Photocopiers, Fax Machines and Other Office Appliances. Mail Merge.